
Click on the "point of reference" on the navball until it displays the relative target velocity. To do this, go back to the staging or docking screen.

You will see an orange/purple pair of arrows.
Go to the map view and use the maneuver tool.

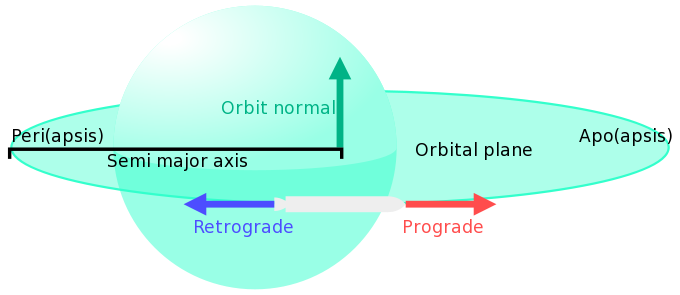
These steps also work for getting into orbit around planets and moons. Follow the steps below to get it right on your first try and feel like a space wizard. NOTE : You may need a mix of normal/antinormal + prograde/retrograde to keep the orbit circular.Īn orbital rendezvous is one of the most challenging maneuvers, requiring a perfect match in orbit and position. Matching orbital inclination is a crucial first step in a rendezvous or docking procedure. It might also help to plan your burns using the orbital maneuver planning system in the map view, where normal and antinormal directions are labeled with purple icons. If you need several burns to get to your desired inclination, remember that if you burn "normal" on one node you need to burn "antinormal" on the other to keep going the same direction. If the craft is passing through the ascending node, where the angle is positive, it needs to burn antinormal (South from an equatorial orbit), while if it's passing through the descending node, and the angle is negative, it should burn normal (North from an equatorial orbit). Both show the same difference, but the descending node show the value as a negative number while the ascending node show the value as a positive one. When hovering over the ascending or descending node markers, it will show the difference in degrees. The direction the craft needs to burn depends on which direction the current orbit is off from the target orbital inclination. You will see two green arrows, labeled "ascending node" and "descending node," where the two orbital planes cross. If you want to orbit on the same plane as another object (planet, ship, etc.), set it as your target in the map view. Raise your periapsis by burning prograde at your apoapsis. Lower your periapsis by burning retrograde at your apoapsis. Raise your apoapsis by burning prograde at your periapsis instead. Lower your apoapsis by burning retrograde (see navball) at your periapsis. In general, burning prograde will make your orbit "larger" and burning retrograde will make it "smaller". A slim design with aerodynamic nose-cones decreases drag and thus increases the maximum speed you can reach without wasting too much thrust on drag. The terminal velocity of your rocket depends on how aerodynamically you build it. Lower velocity wastes delta-V on gravity, higher is wasted on air resistance.
You can save fuel by being close to your terminal velocity during ascent. Accelerate prograde until your periapsis (also visible on your map) is also around 100 km.Cut your engines (hit 'x') and wait until you are getting close to the apoapsis point.Continue to accelerate until your apoapsis (hit M and mouse over the Ap node) is greater than 70 km (the end of Kerbin's atmosphere) - ideally around 100 km.As a rule of thumb, the rocket's nose should point at the rim of the circle of the prograde marker on the navball: You can lean other directions as well (lean north or south to enter a polar orbit), but going east saves fuel by moving with Kerbin's own spin. At that point, begin your gravity turn by slowly leaning east (bearing 90 degrees on your navball, usually "right" from the standard launchpad).Ascend straight up until your speed is about 100 m/s.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
